Sunscreen is an essential step in daily skincare. It not only prevents sunburn but also reduces the risk of skin photoaging by 90%. However, according to a survey by the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), 80% of people have problems with improper use of sunscreen. Based on the latest research in 2025, this article will detail the correct ways to use sunscreen, helping you maximize its sun protection effect.
I. Preparation Before Using Sunscreen
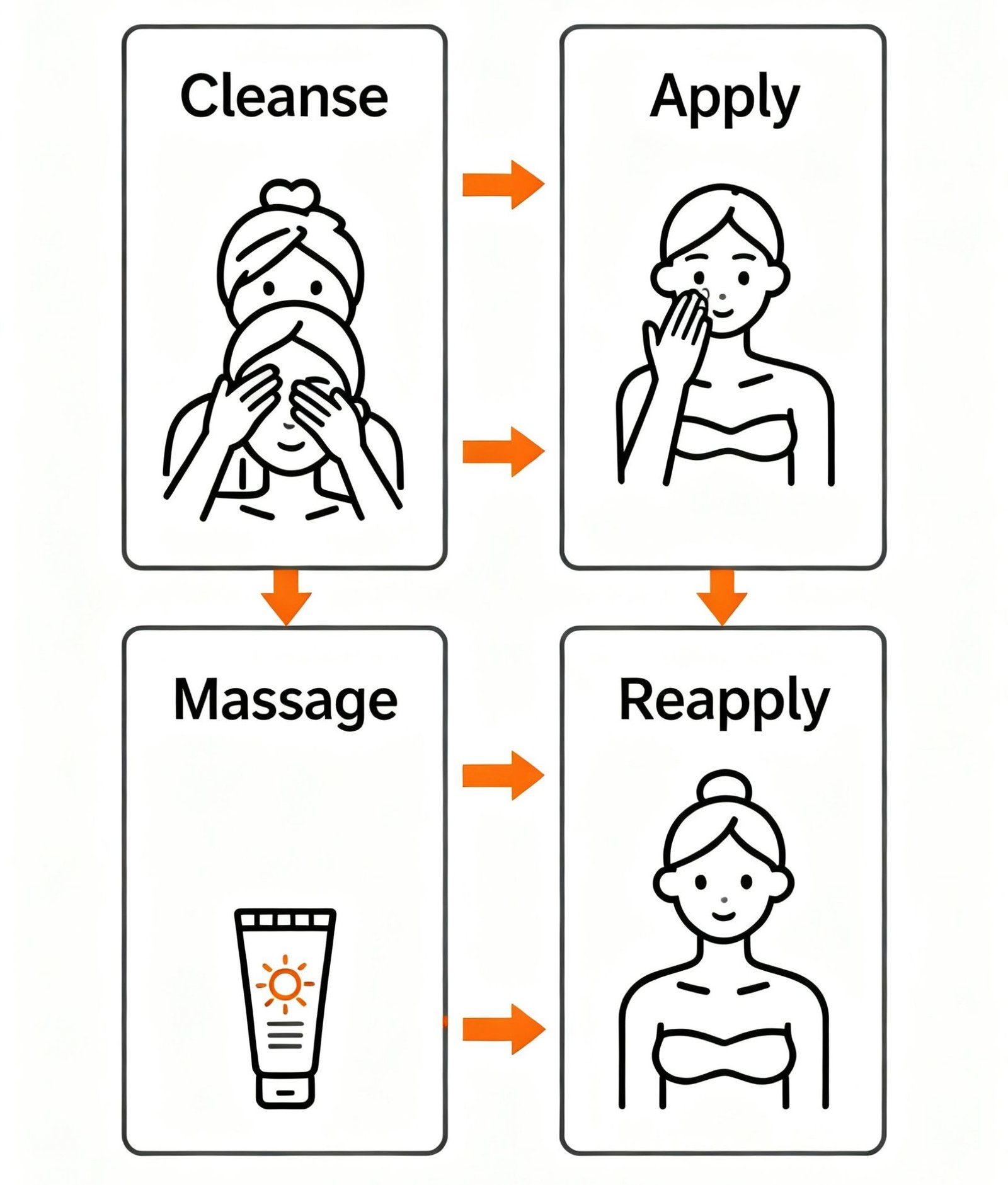
Before applying sunscreen, cleansing the skin is a crucial step. Use a mild facial cleanser to remove oil and dirt, as this prevents sunscreen from being difficult to spread. For oily skin, you can choose an oil-controlling facial cleanser; for dry skin, a moisturizing cleanser is recommended. After cleansing, gently pat your face until it is slightly damp—do not dry it completely. This helps the sunscreen adhere better to the skin.
Note: If you need to apply makeup, wait until the sunscreen has formed a film (usually 15-20 minutes) before proceeding with subsequent steps to avoid damaging the sunscreen film.
II. Correct Amount and Application Method of Sunscreen
The amount of sunscreen used directly affects its protective effect. Most people only use half of the recommended amount, which may reduce the SPF value to less than one-third of the labeled value.
1. Facial Sunscreen Amount
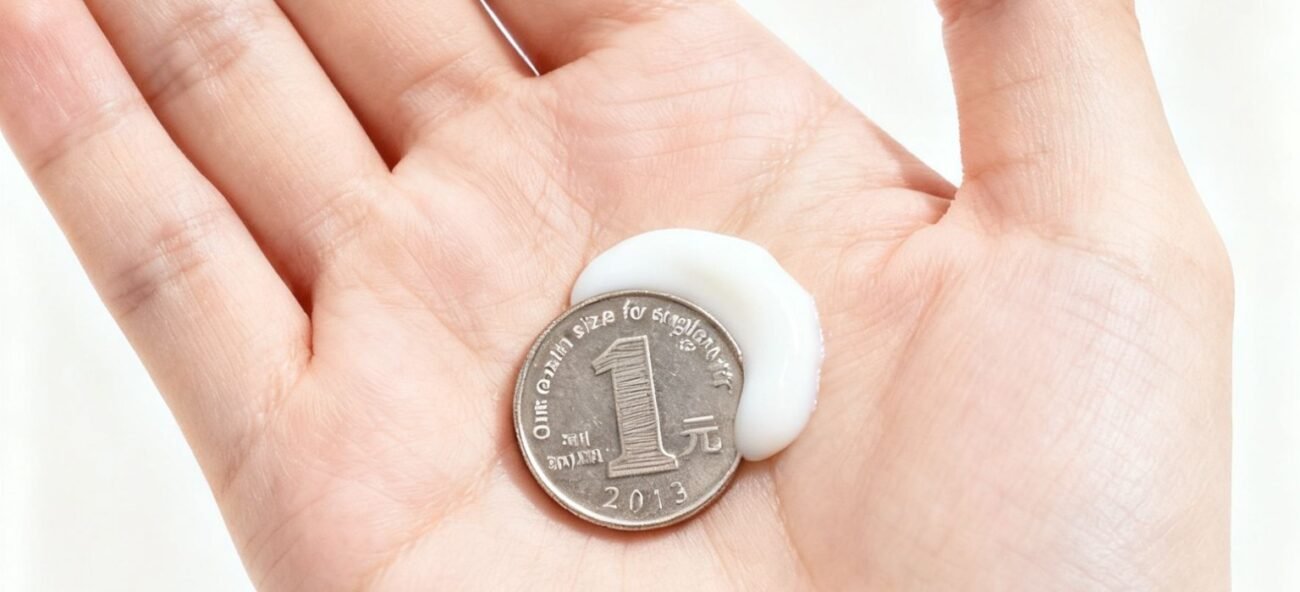
- Standard Amount: Take a coin-sized amount (approximately 0.5ml) of sunscreen, which is sufficient to cover the entire face and neck.
- Dot Application Method: Divide the sunscreen into five dots and apply them to key areas (forehead, tip of the nose, cheeks, chin), then gently spread it with your fingertips.
- Key Areas to Note: Apply extra sunscreen to easily overlooked areas such as the back of the ears, hairline, and neck.

2. Body Sunscreen Amount
- Calculation Formula: Apply 2 milligrams of sunscreen per square centimeter of skin.
- Practical Reference: Approximately 3-4 pumps are needed for both arms, 6-8 pumps for both legs, and about 30ml for a full-body single application (nearly 1/10 of a standard wine bottle).
- Application Tips: For lotion-textured sunscreen, apply it in dots across different body areas and then spread it evenly; for spray-type sunscreen, spray repeatedly until the skin shows a slight sheen.
III. Application Timing for Different Types of Sunscreen
The activation time of sunscreen varies depending on its ingredients, and mastering the correct application timing can maximize its protective effect.
1. Chemical Sunscreen
- Lead Time: Apply 20-30 minutes before going outdoors to allow the active ingredients to fully penetrate the stratum corneum.
- Representative Ingredients:Oxybenzone, avobenzone, etc. Note that some ingredients may cause discomfort for sensitive skin.
2. Physical Sunscreen
- Lead Time: It takes effect immediately, but it is recommended to apply it 10 minutes in advance to ensure even coverage.
- Representative Ingredients: Zinc oxide, titanium dioxide. It is suitable for sensitive skin and children.
- Precautions: It may cause slight whitening on the skin; choosing products with nano-sized particles can reduce this phenomenon.
IV. Reapplication Frequency and Handling of Special Scenarios
Sunscreen is not a one-time solution; it needs to be reapplied promptly based on the environment to maintain continuous sun protection.
1. Regular Reapplication
- Basic Frequency: Reapply every 2-3 hours.
- Reapplication Amount: Half of the initial amount, with extra focus on sweat-prone areas such as the T-zone and the back of the ears.
- Reapplication Tip: When wearing makeup, use a sunscreen spray—hold it 15cm away from the skin, spray, then gently pat to aid absorption.
2. Reapplication in Special Scenarios
- After Swimming/Sweating: Even if you’re using waterproof sunscreen, reapply it immediately after getting out of the water.
- High-Intensity Outdoor Activities: Choose a sunscreen with SPF 50+ and reapply every 1.5 hours.
- Prolonged Indoor Stay Near Windows: Reapply every 4 hours, as UVA can penetrate glass and cause cumulative damage.

V. Sunscreen Guide for Special Populations
People of different age groups and skin types have varying sunscreen needs.
1.Sunscreen for Children
- Under 6 months old: Avoid direct sun exposure; use physical barriers (such as hats, sun-protective clothing, and stroller canopies).
- 6 months old and above: Use children-specific physical sunscreen (containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) with an SPF of 30+.
- Reapplication frequency: Every 2 hours, and reapply immediately after swimming.
2. Sunscreen for Sensitive Skin
- Ingredient Selection: Avoid alcohol, fragrances, and chemical sun filters; prioritize products labeled “hypoallergenic.”
- Recommended Ingredients: Sunscreens containing soothing ingredients such as bisabolol and aloe vera.
- Testing Method: Conduct a 24-hour patch test behind the ear before use.
3. Sunscreen for Pregnant Women
- Ingredient Taboos: Avoid products containing oxybenzone (benzophenone-3), which may disrupt the endocrine system.
- Recommended Choices: Pure physical sunscreen, paired with a wide-brimmed hat and sun-protective clothing.

VI. Common Sunscreen Misconceptions and Solutions
Even people who use sunscreen regularly may have some subtle misconceptions.
Misconception 1: Sunscreen isn’t needed on cloudy days
- Fact: The penetration rate of UVA still reaches 80% on cloudy days, and it is the main cause of skin aging.
- Solution: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30+ every day throughout the year.
Misconception 2: The higher the sun protection factor (SPF), the better
- Fact: SPF 50 blocks 98% of UVB rays, while SPF 100 blocks approximately 99%—the difference is minimal, but the latter may contain more complex ingredients.
- Solution: For daily commuting, SPF 30+ is sufficient; choose SPF 50+ for outdoor activities.
Misconception 3: No other sun protection measures are needed if sunscreen is used
- Fact: Sunscreen should serve as the final line of defense, and its protective effect is better when combined with other measures.
- Solution: Avoid prolonged sun exposure as much as possible between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., and wear sun-protective clothing and hats with a UPF rating of 50+.
VII. Common Questions About Sunscreen Use
Can babies use sunscreen?
Answer: Babies under 6 months old should avoid using sunscreen, and physical barriers such as clothing and hats should be prioritized. For babies aged 6 months and above, baby-specific sunscreen containing zinc oxide can be used, and an SPF of 30+ is sufficient.
Do I need to remove sunscreen?
Answer: It depends on the type of product:
Regular sunscreen: Can be thoroughly cleaned with a mild facial cleanser.
Waterproof sunscreen: It is recommended to use a makeup remover product; especially for physical sunscreen, thorough cleansing should be ensured.
Suggestion for sensitive skin: Choose a non-makeup-removal formula or use micellar water for gentle cleansing.
How to choose the right sun protection factor (SPF) for yourself?
Answer: Choose based on the intensity of your activity:
Daily commute: SPF 30+, PA+++
Outdoor work/sports: SPF 50+, PA++++; the product must also have water-resistant and sweat-resistant properties.
High-altitude areas/snowy environments: SPF 50+, PA++++, as UV intensity increases due to enhanced reflection in these settings.
How long can sunscreen be stored after opening?
Answer: Generally, the shelf life of sunscreen after opening is 12 months, while some products are labeled with a shelf life of 18 months. It is recommended to mark the opening date on the bottle; after the expiration period, the sun protection effect may decrease.
What are the reasons for getting sunburned even after applying sunscreen?
Answer: Possible reasons include:
Insufficient amount applied: The actual sun protection effect is only 1/3 of the labeled value.
Inadequate reapplication: Sweating or wiping damages the sunscreen film.
Improper product selection: Failure to choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen, resulting in insufficient UVA protection.
VIII. 2025 Sunscreen Buying Guide
To choose a sunscreen that suits you, you need to consider your skin type, usage scenario, and ingredient safety.
1. Skin Type Matching
- Oily Skin: Choose lightweight lotions or gel textures labeled “oil-free” or “fresh/non-greasy.”
- Dry Skin: Choose cream-based sunscreens containing moisturizing ingredients (e.g., hyaluronic acid, ceramides).
- Sensitive Skin: Choose fragrance-free and alcohol-free physical sunscreens, and prioritize products that have passed dermatological tests.
2. Ingredient Safety
- Ingredients to Avoid: Controversial ingredients such as oxybenzone (benzophenone-3) and methylisothiazolinone (MIT).
- Recommended Ingredients: Zinc oxide, titanium dioxide (for physical sun protection); ergothioneine, vitamin E (for antioxidant effects).
3. Environmental Considerations
- Reef-safe: Choose products free of oxybenzone and octinoxate to reduce impacts on marine ecosystems.
- Packaging Design: Prioritize sunscreens with recyclable packaging or refillable options to reduce plastic pollution.
Proper use of sunscreen is one of the most effective ways to prevent skin cancer and photoaging. Only by mastering the scientific amount, application method and reapplication skills, and selecting a suitable product based on your personal skin type and usage scenario, can sunscreen truly become a “protective umbrella” for your skin. Remember, sun protection is not just a summer task, but a year-round essential step in skincare. If you want to create your own sunscreen brand, it is recommended to choose DESIFINE OEM, whose low minimum order quantity will support you.